Four Common Reasons for a Stiff Back
We live busy, active lives. In our average day we deal with stress and anxiety that can live in our muscles and make us feel tense. But when is a stiff back caused by an underlying condition beyond tension? Knowing some of the possible causes for back stiffness can help you and your doctor determine the best treatment for you.
While it’s true that sometimes back stiffness can be caused by a disc disorder, chronic condition, or aging process, the stiffness could also be rooted in a muscular issue that may not even be in your actual back. Here are some muscular conditions that may cause back stiffness:
Worried About Your Stiff Back?
Schedule an Appointment
1. Muscle Tightness in Thighs and Hips

We’ve talked before about how hamstring stretches can help alleviate back pain. Tight hamstrings are short hamstrings, and these muscles connect to your lower back. Tightness in your hamstrings can affect the curvature of your lower spine, disrupting the precise alignment of your spine with your pelvis.
Hamstrings may be tight as a result of physical activity, injury, or a failure to stretch before and after exercising. Luckily this problem can be easy to manage at home with some targeted stretching. If you need some help getting started, a physical therapist can help guide you through some basic movements.
Is Your Stiff Back Actually Stiff?
In a study at the University of Alberta’s Faculty of Rehabilitation Medicine, participants were asked how stiff their backs felt to them. After that, the faculty measured the biomechanical status of the participants’ backs.
“There was no relation between biomechanical stiffness and the reported feeling of stiffness,” said Greg Kawchuk, professor and back and spine expert in the Department of Physical Therapy. “What people describe as stiffness is something different than the measurement of stiffness.”
Tasha Stanton, lead author and senior research fellow of pain neuroscience at the University of South Australia, said that the feeling of stiffness may be a protective construct that is created by our nervous system.
“It’s our body’s way of protecting ourselves, possibly from strain, further injury or more pain,” she said.
2. Tight Hip Flexors
Related Content:
Should I Run with Back Pain?
Running or jogging is a great way to stay healthy, and a great way to get a workout when going to the gym isn’t an option. But what if running hurts your back? Or what if your back hurts when you’re done? Why does this happen?
 Between long commutes in the car, long days in the office, and binge-watching our favorite shows on Netflix, we tend do more sitting than our bodies are built to do. Sitting for long periods of time increases the pressure on the discs in your spine, causes the muscles in your upper and lower back to lose strength, and can decrease the supply of nutrients to your spinal tissue.
Between long commutes in the car, long days in the office, and binge-watching our favorite shows on Netflix, we tend do more sitting than our bodies are built to do. Sitting for long periods of time increases the pressure on the discs in your spine, causes the muscles in your upper and lower back to lose strength, and can decrease the supply of nutrients to your spinal tissue.
Avoiding back stiffness and pain from prolonged sitting can be allayed by sitting with the correct posture and performing a few basic movements and stretches to keep your muscles working. Roll your shoulders back with the ears over the shoulders and the upper arms parallel to your torso. While sitting in an office chair try to avoid constant use of the backrest and sit upright to activate your core muscles.
3. Improper Sitting Posture
Between long commutes in the car, long days in the office, and binge-watching our favorite shows on Netflix, we tend do more sitting than our bodies are built to do. Sitting for long periods of time increases the pressure on the discs in your spine, causes the muscles in your upper and lower back to lose strength, and can decrease the supply of nutrients to your spinal tissue.
Avoiding back stiffness and pain from prolonged sitting can be allayed by sitting with the correct posture and performing a few basic movements and stretches to keep your muscles working. Roll your shoulders back with the ears over the shoulders and the upper arms parallel to your torso. While sitting in an office chair try to avoid constant use of the backrest and sit upright to activate your core muscles.
Related Content:
Proper Posture for Back Pain Relief?
4. Spine Problems that Cause Back Stiffness
Up until here we’ve discussed some basic stretches and postural changes you can make to help relieve and prevent back stiffness. But what if the condition is deeper than muscular? Below is a list of some other common causes of tightness in your lower back.
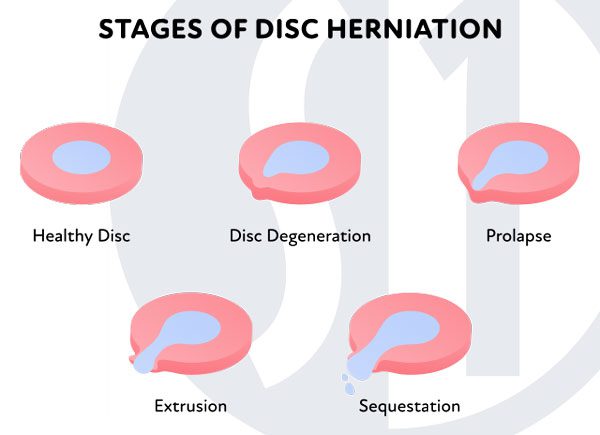
- Herniated or ruptured discs: This is a flattening and bulging out or rupturing of the discs that sit between the vertebrae.
- Sciatica: This is a form of radiculopathy that involves compression of the sciatic nerve running down the back.
- Spinal stenosis: This is narrowing of the spinal column, which puts pressure on the nerves and spinal cord.
- Spondylolisthesis: This occurs when the vertebrae of the lower back come out of place and pinch nearby nerves.
- Arthritis: This is an inflammatory condition that affects joints throughout the body, including the back.
If the pain and stiffness lasts more than 3 to 4 week it may be from these conditions. It’s best to discuss long-term or debilitating pain with a doctor who may recommend physical therapy, pain management therapies, or minimally-invasive treatments. Your doctor will guide you through the diagnosis, imaging, and treatment of these conditions based on the root cause of your back stiffness.